The first trimester of pregnancy is an exciting yet critical time for both the mother and baby. During this period, antenatal tests are performed to assess the health of the mother, confirm the pregnancy, and identify any potential risks early. These tests are an essential part of prenatal care, enabling healthcare providers to offer tailored support and guidance throughout the pregnancy.
This guide explains the various antenatal tests conducted in the first trimester, when they are offered, who should consider them, and how they contribute to a healthy pregnancy.
Why Are First Trimester Antenatal Tests Important?
First trimester antenatal tests are designed to:
Confirm the pregnancy and estimate its progress.
Screen for genetic or chromosomal abnormalities.
Assess the mother’s overall health and identify potential complications.
Provide a baseline for tracking health changes in later stages.
These tests are part of routine antenatal care in the UK and are typically initiated during the first antenatal appointment, known as the booking appointment, which occurs between weeks 8 and 10.
Routine First Trimester Tests
1. Booking Appointment Overview
The booking appointment is the foundation of antenatal care, where healthcare providers collect detailed information about the mother’s medical history, lifestyle, and potential risk factors. This visit includes:
Setting a due date based on the last menstrual period.
Discussing lifestyle adjustments, such as nutrition, exercise, and the importance of antenatal vitamins.
Providing information about antenatal scans and other tests.
2. Blood Tests
Blood tests are a cornerstone of first trimester antenatal care. These tests assess maternal health and screen for potential complications.
What Blood Tests Are Performed?
Blood Group and Rh Factor: Determines the mother’s blood type and Rh status. If the mother is Rh-negative, anti-D injections may be required later to prevent complications.
Full Blood Count (FBC): Checks for anaemia, infections, and platelet levels.
Infectious Disease Screening: Includes tests for HIV, syphilis, and hepatitis B, all of which can affect the baby if untreated.
Rubella Immunity: Confirms whether the mother is immune to rubella, which can cause severe birth defects if contracted during pregnancy.
Who Gets These Tests?
These blood tests are standard for all pregnant women in the UK as part of routine pregnancy care.
3. Urine Tests
Urine samples are collected to monitor for conditions that could pose risks during pregnancy.
What Are They Checking For?
Protein Levels: High levels can indicate pre-eclampsia, a serious condition that may develop later in pregnancy.
Glucose Levels: Elevated glucose may signal early gestational diabetes.
Bacteria: Identifies urinary tract infections (UTIs), which are common during pregnancy and require prompt treatment.
Who Needs These Tests?
All pregnant women will have urine samples tested at their booking appointment and at subsequent antenatal checkups.
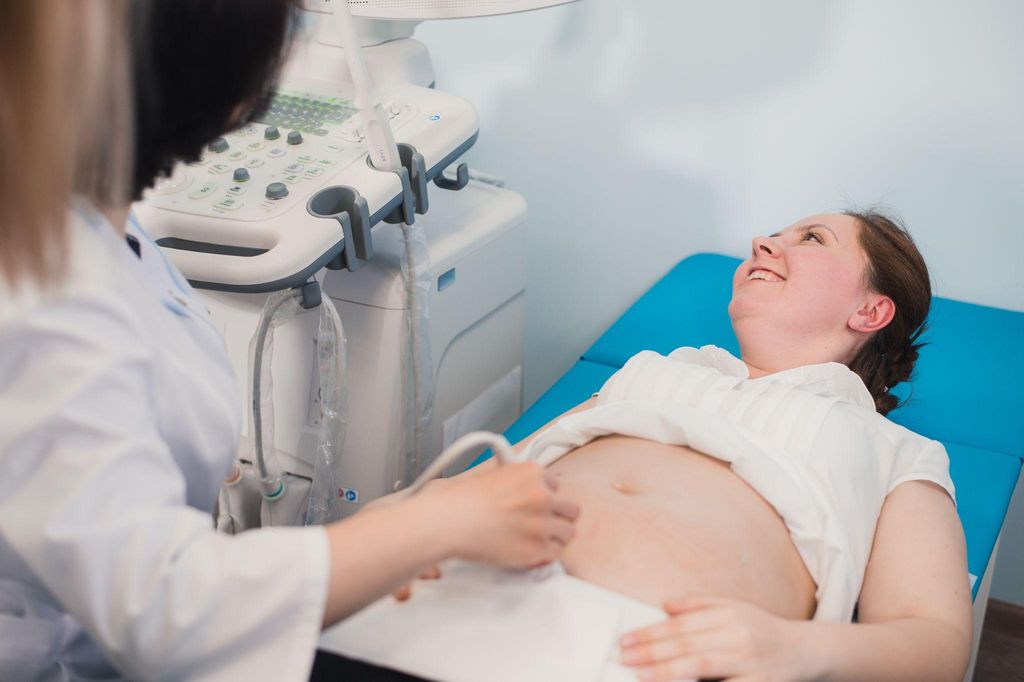
4. Early Ultrasound (Dating Scan)
The early ultrasound, or dating scan, is typically performed between weeks 10 and 14. It confirms the pregnancy and provides key information about its progress.
What Does the Scan Check For?
Confirms the presence of a foetus and estimates gestational age.
Checks for multiple pregnancies.
Ensures the pregnancy is located within the uterus (to rule out ectopic pregnancy).
Who Should Get It?
This scan is routinely offered to all pregnant women in the UK as part of standard antenatal care.
Screening Tests for Chromosomal Abnormalities
In addition to routine tests, first trimester screenings assess the baby’s risk for certain genetic conditions.
1. Combined Test
The combined test is the primary screening method for chromosomal abnormalities, offered between weeks 10 and 14. It includes:
Nuchal Translucency Ultrasound: Measures the fluid at the back of the baby’s neck.
Blood Test: Analyses pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A (PAPP-A) and human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) levels.
These measurements estimate the baby’s risk of:
Down’s syndrome (Trisomy 21).
Edwards’ syndrome (Trisomy 18).
Patau’s syndrome (Trisomy 13).
Who Should Consider the Combined Test?
The combined test is offered to all pregnant women in the UK. It is non-invasive and provides valuable information about the likelihood of chromosomal abnormalities.
2. Non-Invasive Prenatal Testing (NIPT)
NIPT is a more advanced screening option available privately in the UK. It analyses fragments of the baby’s DNA in the mother’s blood to assess chromosomal abnormalities.
When Is NIPT Recommended?
For women who receive high-risk results from the combined test.
For women with a family history of genetic conditions.
For older mothers (typically over 35), as age increases the risk of chromosomal abnormalities.
Advantages of NIPT:
Highly accurate for detecting Down’s syndrome, with over 99% sensitivity.
Non-invasive, posing no risk to the baby.
Specialised Tests for High-Risk Pregnancies
If routine or screening tests indicate higher risks, additional testing may be recommended.
Chorionic Villus Sampling (CVS)
CVS involves collecting a small sample of placental tissue to diagnose genetic conditions definitively. It is typically performed between weeks 10 and 13.
When Is CVS Offered?
If the combined test or NIPT indicates a high risk of chromosomal abnormalities.
If there is a family history of genetic conditions, such as cystic fibrosis or sickle cell disease.
Risks and Benefits:
Provides a definitive diagnosis.
Slight risk of miscarriage (approximately 1 in 100).
Preparing for First Trimester Antenatal Tests
How to Prepare:
Schedule Early: Book your first antenatal clinic visit as soon as you know you’re pregnant.
Ask Questions: Use your booking appointment to discuss the purpose and benefits of each test.
Follow Instructions: Some tests, such as fasting for glucose tests, may require preparation.
Stay Informed: Attend antenatal education sessions to understand the significance of these tests.
Lifestyle Tips to Support a Healthy First Trimester
While antenatal tests are vital, a healthy lifestyle plays an equally important role in pregnancy care.
Nutrition
Eating a balanced diet and taking antenatal vitamins, particularly folic acid, supports the baby’s development and reduces the risk of neural tube defects.
Physical Activity
Engage in gentle exercises like yoga during pregnancy to improve circulation, reduce stress, and maintain strength.
Stress Management
Incorporating relaxation during pregnancy, such as meditation or prenatal massage, can ease anxiety and promote overall well-being.
First trimester antenatal tests are a critical part of ensuring a healthy pregnancy for both mother and baby. From routine blood and urine tests to advanced screenings for chromosomal abnormalities, these assessments provide essential insights into your pregnancy journey. Regular antenatal appointments and open communication with your healthcare provider ensure you receive the right tests at the right time. Combined with a healthy lifestyle and informed decision-making, these tests form the foundation for a safe and joyful pregnancy.
References
- The Ultimate Antenatal Classes
Prepare for labour, birth, and baby care with nine experts, including senior NHS midwives and an award-winning obstetrician!
https://unii.com/en/journey/ultimate-antenatal-classes