Introduction
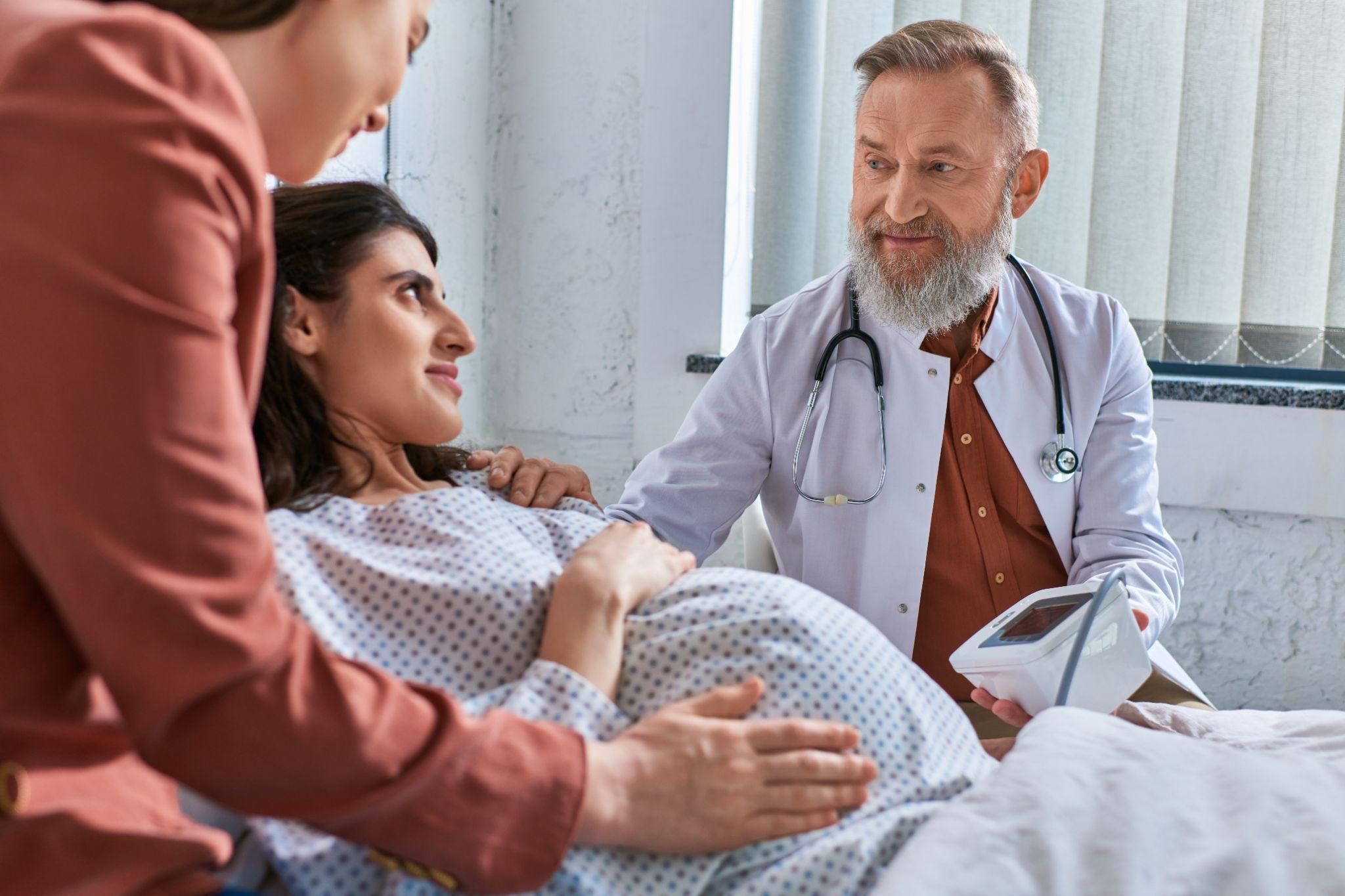
Pregnancy is a life-changing experience, but for high-risk pregnancies, it can bring additional challenges and concerns. Early antenatal diagnosis plays a critical role in ensuring the health and safety of both mother and baby, especially in situations where complications are more likely. By identifying potential issues early, healthcare providers can tailor prenatal care to address specific risks, offering reassurance and support to expectant parents.
This article explores the importance of early antenatal diagnosis for high-risk pregnancies, the diagnostic tools available, and how these tests integrate into comprehensive antenatal care plans. Additionally, we’ll discuss supportive practices like antenatal yoga, nutritional guidance, and antenatal education to help parents navigate this journey.
What Is a High-Risk Pregnancy?
A high-risk pregnancy is one where the mother or baby faces an increased likelihood of complications. Factors contributing to high-risk pregnancies include maternal age (over 35), pre-existing health conditions (e.g., diabetes, hypertension), multiple pregnancies (twins or more), and a history of pregnancy complications.
Why Early Diagnosis Matters
Timely Intervention: Early detection allows healthcare providers to manage risks effectively.
Personalised Care: Enables customised monitoring and treatment plans.
Informed Decisions: Parents can prepare emotionally and practically for potential outcomes.
Key Antenatal Diagnostic Tools for High-Risk Pregnancies
1. Routine Blood Tests
Blood tests are often the first step in early antenatal diagnosis, providing insights into maternal and foetal health.
What They Detect
Anaemia: Managed with iron-rich foods or antenatal vitamins.
Infections: Such as syphilis, hepatitis B, and HIV.
Blood Type and Rhesus Factor: Ensures compatibility between mother and baby.
Blood tests are typically conducted during the initial antenatal appointments and repeated throughout the pregnancy as needed.
2. Non-Invasive Prenatal Testing (NIPT)
NIPT is a safe, accurate blood test that analyses foetal DNA present in the mother’s bloodstream.
What It Screens For
Chromosomal conditions like Down syndrome (Trisomy 21) and Edwards syndrome (Trisomy 18).
Sex chromosome abnormalities.
Why It’s Beneficial for High-Risk Pregnancies
Safe and non-invasive.
Detects issues as early as 10 weeks into the pregnancy.
Reduces the need for more invasive tests in many cases.
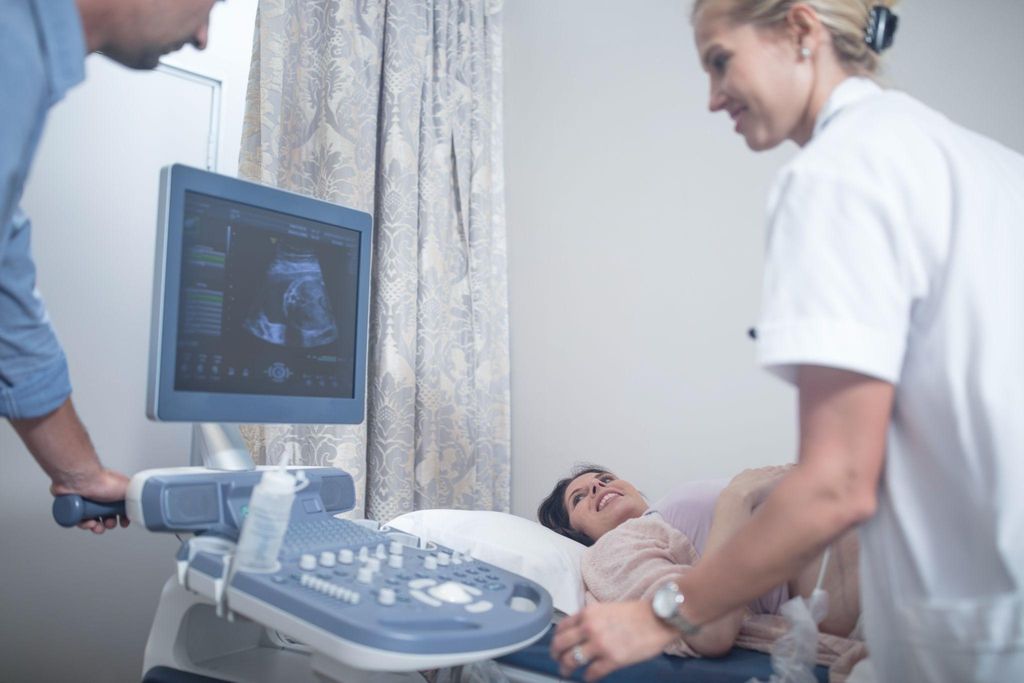
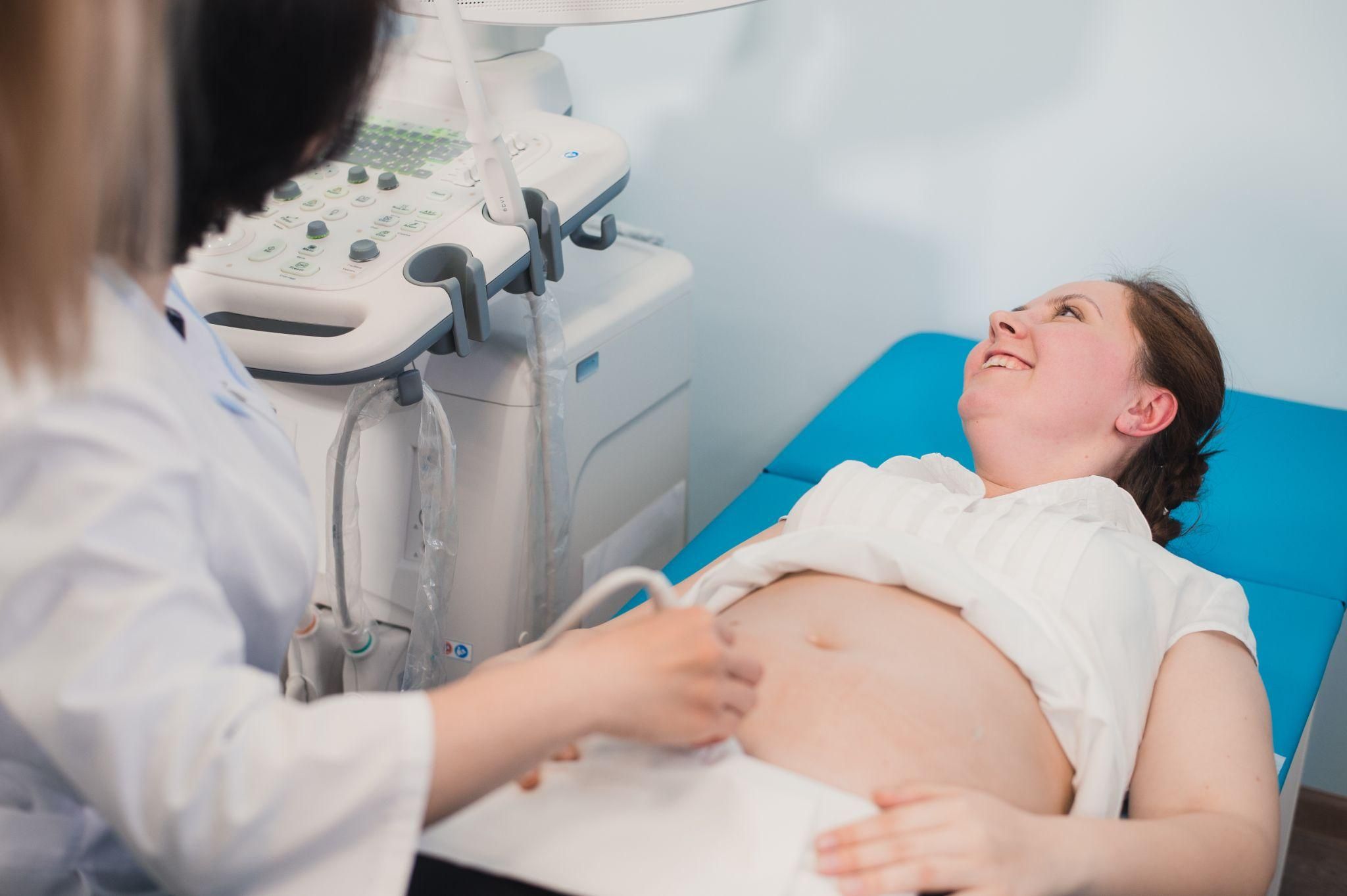
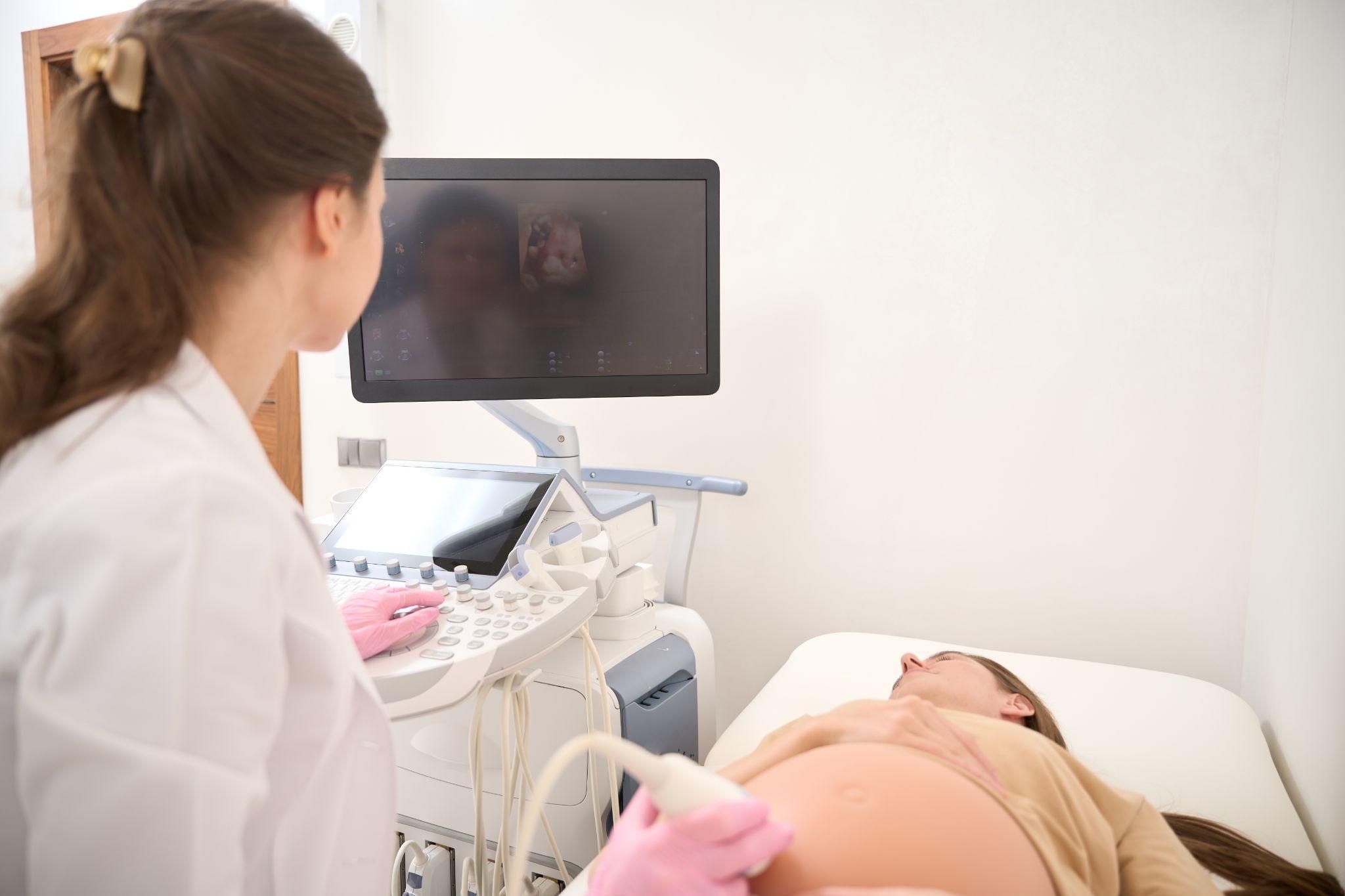
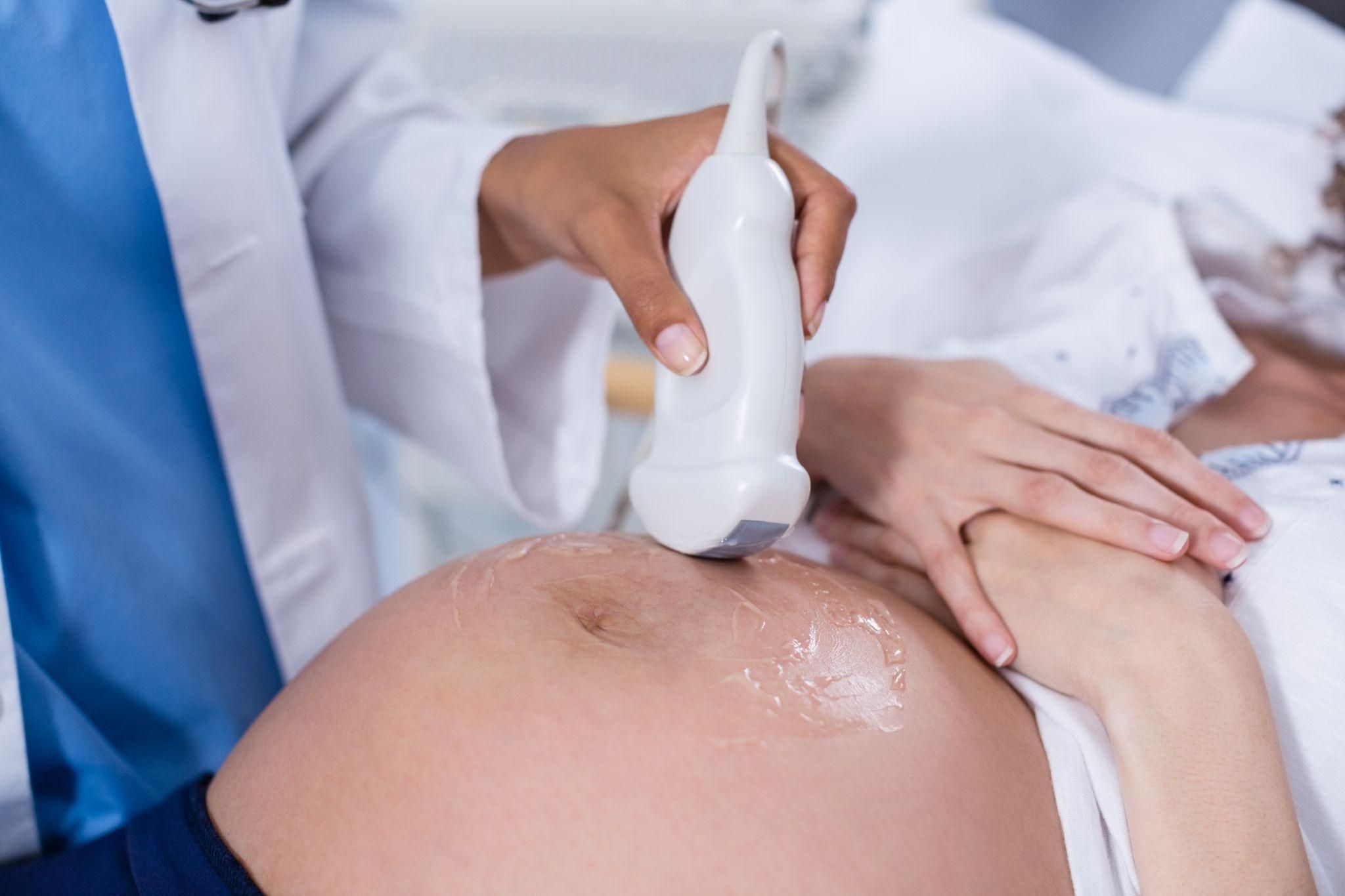
3. Ultrasound Scans
Ultrasounds are essential for monitoring foetal development and identifying structural abnormalities.
Types of Scans
Dating Scan: Confirms gestational age and due date.
Anomaly Scan: Conducted at 18-20 weeks to detect physical abnormalities.
Growth Scan: Monitors the baby’s size and placental health in later stages.
Ultrasounds are non-invasive and painless, making them a cornerstone of antenatal care for all pregnancies, particularly high-risk ones.
4. Specialised Diagnostic Tests
For pregnancies requiring closer scrutiny, invasive diagnostic tests may be recommended.
Amniocentesis
Performed between 15-20 weeks to test amniotic fluid for chromosomal or genetic abnormalities.
Often recommended after abnormal screening results.
Chorionic Villus Sampling (CVS)
Conducted at 10-13 weeks to test placental tissue.
Offers earlier results than amniocentesis.
How Early Diagnosis Enhances Pregnancy Care
1. Tailored Monitoring and Treatment
Early antenatal diagnosis allows for personalised pregnancy care, addressing unique risks. Examples include:
Gestational Diabetes: Managed through diet, exercise, and medication.
Placenta Previa: Requires planning for delivery to avoid complications.
2. Psychological Support
Knowing potential risks in advance reduces uncertainty and anxiety, especially when paired with antenatal support such as counselling or group classes.
The Role of Antenatal Clinics and Appointments
Regular antenatal checkups are essential for high-risk pregnancies. These visits provide opportunities to:
Monitor maternal health (e.g., blood pressure, weight).
Discuss test results and next steps.
Access additional services, such as antenatal education or referrals to specialists.
Antenatal Clinics in the UK
The NHS offers comprehensive support for high-risk pregnancies, ensuring access to diagnostic tests and specialist care. Parents can also explore private clinics for additional services like NIPT or 4D ultrasounds.
Complementary Practices to Support High-Risk Pregnancies
1. Antenatal Yoga
Antenatal yoga is a safe, gentle form of exercise that benefits both physical and emotional health.
Benefits for High-Risk Pregnancies
Improves flexibility and circulation.
Reduces stress and promotes mindfulness.
Strengthens muscles needed for labour.
Joining pregnancy yoga classes tailored for high-risk pregnancies ensures exercises are appropriate and safe.
2. Prenatal Massage
For managing physical discomforts like back pain or swelling, prenatal massage offers significant relief.
Massage for Pregnancy
Enhances relaxation, reducing stress hormones.
Improves sleep quality.
Promotes overall well-being during a challenging pregnancy.
Always consult your healthcare provider before starting massage therapy to ensure it’s safe for your situation.
3. Nutritional Support
High-risk pregnancies often require enhanced nutritional care. Supplements like antenatal vitamins (e.g., folic acid, iron) and a balanced diet are critical for maintaining maternal and foetal health.
Educational Resources for High-Risk Pregnancies
1. Antenatal Classes
Attending antenatal classes near me provides practical information on managing high-risk pregnancies, preparing for delivery, and postpartum recovery.
What to Expect
Insights into diagnostic tests and their implications.
Guidance on labour options, including planned caesareans.
Tips for newborn care and breastfeeding.
2. Emotional Support Networks
Parenting groups and online forums for high-risk pregnancies can offer comfort and advice from others with similar experiences.
FAQs About Early Antenatal Diagnosis
1. Are Antenatal Tests Safe for High-Risk Pregnancies?
Yes, non-invasive tests like NIPT and ultrasounds are completely safe. Invasive tests, such as amniocentesis, carry minimal risks but are performed only when necessary.
2. What If Results Indicate a Problem?
Your healthcare provider will discuss the findings in detail and provide options for further testing, treatment, or specialised care plans.
3. Can Complementary Practices Help?
Yes, activities like yoga for pregnancy and relaxation techniques support emotional and physical well-being, complementing medical care.
Conclusion
Early antenatal diagnosis is a lifeline for high-risk pregnancies, enabling healthcare providers to identify and address potential complications with precision. Through tools like NIPT, ultrasounds, and personalised care plans, these diagnostics give parents the knowledge they need to navigate their pregnancy confidently.
When combined with regular antenatal appointments, supportive practices like antenatal yoga and nutritional care, and resources like antenatal classes, parents can embrace their journey with preparation and peace of mind. By prioritising early diagnosis and proactive care, high-risk pregnancies can lead to successful and healthy outcomes.
Sources
National Health Service (2023). Antenatal Care for High-Risk Pregnancies. Link
Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists (2022). Prenatal Testing and High-Risk Care Guidelines. Link
Tommy’s (2023). Managing High-Risk Pregnancies: A Guide for Parents. Link
References
- The Ultimate Antenatal Classes
Prepare for labour, birth, and baby care with nine experts, including senior NHS midwives and an award-winning obstetrician!
https://unii.com/en/journey/ultimate-antenatal-classes